🖐🏻 免责声明
本教程仅供学习交流使用,严禁用于商业用途和非法用途,否则由此产生的一切后果均与作者无关,请各读者自觉遵守相关法律法规。
# abi编码解码
# ABI编码
我们将用编码4个变量,他们的类型分别是uint256, address, string, uint256[2]:
uint x = 10;
address addr = 0x7A58c0Be72BE218B41C608b7Fe7C5bB630736C71;
string name = "0xAA";
uint[2] array = [5, 6];
# abi.encode
他将每个参数填充为32字节的数据,并拼接在一起。如果你要和合约交互,你要用的就是
abi.encode。
function encode() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encode(x, addr, name, array);
return result;
}
编码的结果为0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,由于abi.encode将每个数据都填充为32字节,中间有很多0。
# abi.encodePacked
将给定参数根据其所需最低空间编码。它类似
abi.encode,但是会把其中填充的很多0省略。比如,只用1字节来编码uint类型。当你想省空间,并且不与合约交互的时候,可以使用abi.encodePacked,例如算一些数据的hash时。
function encodePacked() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodePacked(x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a7a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c713078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000050000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006,由于abi.encodePacked对编码进行了压缩,长度比abi.encode短很多。
# abi.encodeWithSignature
与
abi.encode功能类似,只不过第一个参数为函数签名,比如"foo(uint256,address)"。当调用其他合约的时候可以使用。
function encodeWithSignature() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodeWithSignature("foo(uint256,address,string,uint256[2])", x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0xe87082f1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,等同于在abi.encode编码结果前加上了4字节的函数选择器说明。 说明: 函数选择器就是通过函数名和参数进行签名处理(Keccak–Sha3)来标识函数,可以用于不同合约之间的函数调用
# abi.encodeWithSelector
与
abi.encodeWithSignature功能类似,只不过第一个参数为函数选择器,为函数签名Keccak哈希的前4个字节。
function encodeWithSelector() public view returns(bytes memory result) {
result = abi.encodeWithSelector(bytes4(keccak256("foo(uint256,address,string,uint256[2])")), x, addr, name, array);
}
编码的结果为0xe87082f1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0000000000000000000000007a58c0be72be218b41c608b7fe7c5bb630736c7100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043078414100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000,与abi.encodeWithSignature结果一样。
# ABI解码
# abi.decode
abi.decode用于解码abi.encode生成的二进制编码,将它还原成原本的参数。
function decode(bytes memory data) public pure returns(uint dx, address daddr, string memory dname, uint[2] memory darray) {
(dx, daddr, dname, darray) = abi.decode(data, (uint, address, string, uint[2]));
}
# ABI的使用场景
- 在合约开发中,ABI常配合call来实现对合约的底层调用。
bytes4 selector = contract.getValue.selector;
bytes memory data = abi.encodeWithSelector(selector, _x);
(bool success, bytes memory returnedData) = address(contract).staticcall(data);
require(success);
return abi.decode(returnedData, (uint256));
- ethers.js中常用ABI实现合约的导入和函数调用。
const wavePortalContract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, contractABI, signer);
/*
* Call the getAllWaves method from your Smart Contract
*/
const waves = await wavePortalContract.getAllWaves();
- 对不开源合约进行反编译后,某些函数无法查到函数签名,可通过ABI进行调用。
0x533ba33a() 是一个反编译后显示的函数,只有函数编码后的结果,并且无法查到函数签名
这种情况无法通过构造interface接口或contract来进行调用,可以通过ABI函数选择器来调用:
bytes memory data = abi.encodeWithSelector(bytes4(0x533ba33a));
(bool success, bytes memory returnedData) = address(contract).staticcall(data);
require(success);
return abi.decode(returnedData, (uint256));
# 编译后的json文件
在Solidity编译器生成的JSON输出文件中,bytecode 和 deployedBytecode 分别代表了智能合约的不同编译阶段和用途的字节码:
# bytecode
- 这是智能合约未经部署时的原始字节码,通常被称为未链接的字节码(Unlinked Bytecode)。它包含了合约的所有逻辑、结构以及可能的库引用(如果合约依赖于其他库),但并未包含具体的库地址或其他外部合约地址。这种字节码主要用于合约的部署阶段。
# deployedBytecode
deployedBytecode则是智能合约在实际部署到以太坊区块链上之后的最终形式,即已部署字节码(Deployed Bytecode)。它与
bytecode的主要区别在于:- 链接(Linking):如果合约依赖于外部库,部署字节码会将库的逻辑替换为指向已部署库地址的跳转指令。这意味着所有库的调用现在都指向了实际存在于区块链上的库合约地址。
- 初始化(Initialization):部署字节码还包括了合约部署时执行的构造函数(constructor)逻辑。这部分逻辑仅在部署时执行一次,用于设置合约的初始状态。在部署完成后,构造函数部分不再存在于合约的运行时代码中。
总结来说,bytecode 是智能合约原始、未完全确定状态的字节码,适用于准备部署阶段;而 deployedBytecode 是经过链接(如果有库依赖)、执行了构造函数且已经部署到区块链上的最终形态的字节码,反映了合约在链上的实际执行环境。在开发过程中,通常使用 bytecode 进行预部署测试或准备部署交易,而 deployedBytecode 则用于分析已部署合约的行为或进行合约间的交互。
# 消息签名与验签
# 1.eth_sign所需要的参数实现过程,实际不需要操心
其实eth_sign请求和ethers.js的wallet的signMessage方法都封装好了,不需要拼装该参数,直接传原始字符串就行(eth_sign可能需要原始字符串的hex值)
# solidity版本
// SPDX-License-Identifier: SEE LICENSE IN LICENSE
pragma solidity >=0.8.0 <0.9.0;
contract Signature {
function getEthSignedMessageHash(
string memory _message
) public pure returns (bytes32) {
//这可能是一种约定俗成的写法,先将_message hash为固定32字节,这样下面可以写固定长度32,因为solidity获取字符串长度比较复杂
bytes32 _messageHash = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(_message));
return
//"\x19Ethereum Signed Message:\n32"这一串为了与转账信息区别开来,32代表_messageHash的长度,这里就是32
keccak256(
abi.encodePacked(
"\x19Ethereum Signed Message:\n32",
_messageHash
)
);
}
}
# ethers版本
const { keccak256, getBytes, hashMessage, toUtf8Bytes } = require("ethers");
// 1.先将Hello转为keccak256的hash,是个0x形式的字符串
const beforeEthHash = keccak256(toUtf8Bytes("Hello"));
console.log("beforeEthHash", beforeEthHash);
// 2.再将这个十六进制字符串getBytes得到字节数组
const beforeEthHashBytes = getBytes(beforeEthHash)//这里为什么要以数组形式传入,而不是直接给0x的hex字符串,因为下面hashMessage方法会判断传入参数是否是字符串,是字符串,会直接将这个0x的hex字符串转为字符串本身对应的字节数组
//这么说有点绕,我举个例子,我们都知道"a"的字节形式为十进制的assic码是97,对应的十六进制字节表示就是0x61,但是字符串"0x61"这个字符串而言,若将他转为字节数组,"a" 和 "0x61"肯定是两个不同的东西,所以我们需要getBytes方法,将对应的"0x61"这个hex恢复他的本体"a"对应的字节数组
const sigFromEthers = hashMessage(beforeEthHashBytes);
console.log("afterTheHash", sigFromEthers);
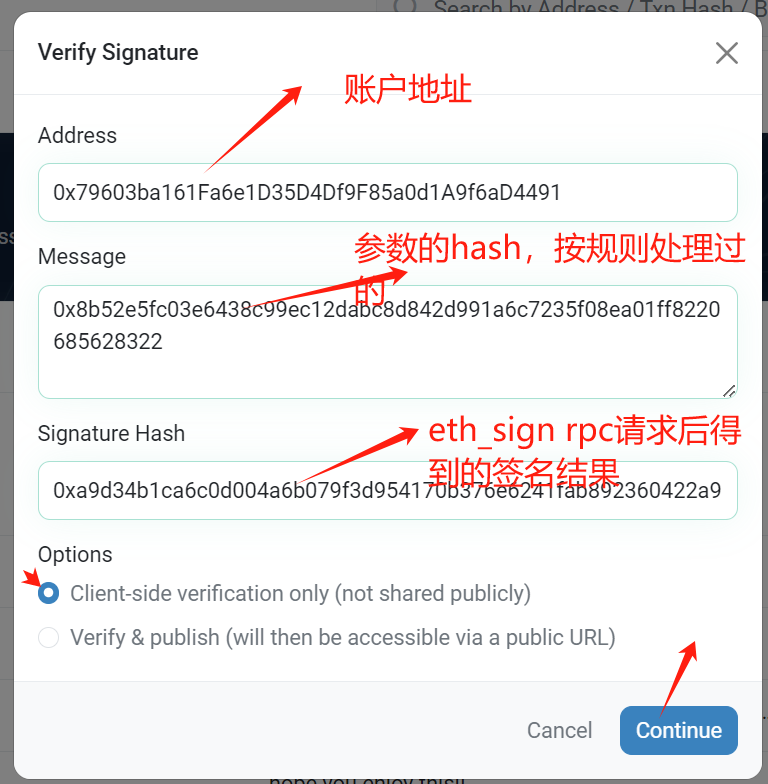
# 2.eth_sign Rpc请求
参数
{
jsonrpc: "2.0", // 指定JSON-RPC的版本
method: "eth_sign", // 请求的方法名,
params: [address, 字符串的hex值], // 方法参数为空
id: 1337, // 请求的唯一标识,使用chainId
};
返回值
{
"id": 1337,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": "0xa9d34b1ca6c0d004a6b079f3d954170b376e6241fab892360422a93fe960df14737f4423ba5e48eea28fd48732ee1bd908c2a4c7d37d1f7ceda4a523ae15905600"//这个就是最后的签名结果
}
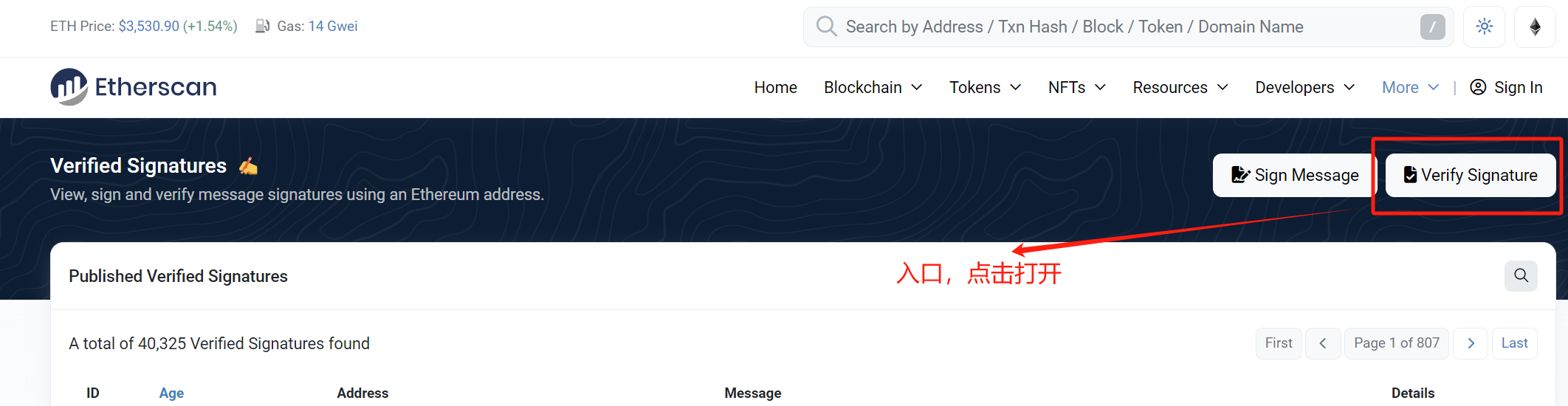
# 3.在线验签
验签地址:https://etherscan.io/verifiedSignatures
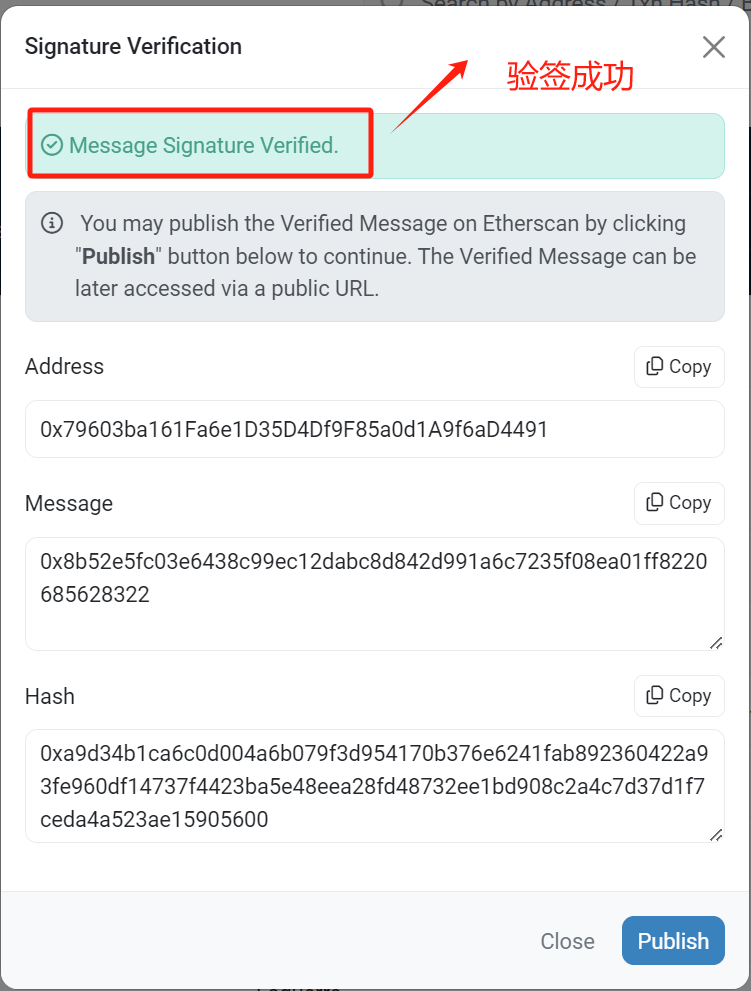
# 4.ethers验签
const {
keccak256,
getBytes,
hashMessage,
toUtf8Bytes,
toUtf8String,
Wallet,
hexlify,
JsonRpcProvider,
} = require("ethers");
const str = "Hello";
const sig = hexlify(toUtf8Bytes(str));//得到hex字符串
//getBytes(sig) 将hex字符串转为bytes数组
const address = await ethers.verifyMessage(getBytes(sig), signature);
# 插槽数据
# 状态变量
- 常量不会存储在 Slot 中。
- Slot是按顺序存储状态变量,从0开始依次编号为1、2、3等...
- 由于 Slot 长度为 32 字节,因此当状态变量类型所需空间不足 32 字节时,我们会将它们放在一起,这样可以更节省空间
# 大于32字节数据存储
- 大于bytes32的数据,不会存储在相应的状态变量插槽里
- 大于bytes32的数据,状态变量的插槽仅存储数据字节的长度
- 大于bytes32的数据,数据存储一系列连续插槽里。其中,起始插槽是状态变量对应插槽的哈希(keccak256)
# Array
# 静态数组(定长数组)
每一个元素占用一个slot
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
//静态数组和动态数组的存储在插槽,它们之间存在差异
contract SlotArrayExample {
//slot0 = 1;
//slot1 = 2;
//slot2 = 3;
//slot3 = 4;
//slot4 = 5;
uint[5] private iArray = [1,2,3,4,5];
//slot5 = Hello
string private name = "Hello";
//获取小于或等于32个字节插槽的数据
function getBytes32BySlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(slot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
}
# 动态数组
对应插槽存的是数组长度,获取方式同超过32字节的变量,
- 对应插槽 uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot)))后,得到真正存值的插槽位置,
- 然后第一步的值+数组下标,依次取得每个位置的元素数据。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
//静态数组和动态数组的存储在插槽,它们之间存在差异
contract SlotArrayExample {
//slot0 = 1;
//slot1 = 2;
//slot2 = 3;
//slot3 = 4;
//slot4 = 5;
uint[5] private iArray = [1,2,3,4,5];
//slot5 = Hello
string private name = "Hello";
//slot6 = 5 数组的长度
uint[] private iArrayDynamic = [5,4,3,2,1];
//slot7 = 3
uint8[] private i8ArrayDynamic = [1,2,3];
//slot8 = 2
string[] private stringArrayDynamic = ["Hello","World"];
//slot9 = 2;
string[] private stringGreatThan32ArrayDynamic = ["HelloHelloHelloHelloHelloHello012345678","WorldWorldWorldWorldWorldWorld012345"];
//获取小于或等于32个字节插槽的数据
function getBytes32BySlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(slot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//计算储存数据插槽
function calculateLocation(uint256 slot, uint256 index) public pure returns (uint256) {
return uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot))) + index ;
}
//Hash插槽
function keccak256Slot(uint256 slot) public pure returns (uint256) {
// bytes32 paddedSlot = bytes32(slot);
bytes32 baseSlot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot));
uint256 iBaseSlot = uint256(baseSlot);
return iBaseSlot;
}
}
# Struct
- Struct 结构类型,它会根据结构中包含的属性数量进行内存分配
- 每个属性占用一个插槽
- 具体取值看这个属性的值是否超过32个字节
- Struct 结构数组,也是连续插槽储存
- 对应插槽 uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot)))后,得到真正存值的插槽位置
- 属性连续存储,比如我们User 有两个属性,User [] private users 存了三个user,那 为了取得user0.name,user0.age,user1.name,user1.age,user2.name,user2.age, 我们需要加的index值依次为0,1,2,3,4,5
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract SlotStructExample {
uint256 a = 100; // slot 0
struct User {
string name; //
uint256 age; //
}
uint256 b = 101; // slot 1
User private user; // slot 2,3
uint256 c = 102 ; // slot 4
User [] private users; // slot 5
//设置用户
function setUser(User calldata _user) public {
user = _user;
}
//add user
function addUser(User calldata _user) public {
users.push(_user);
}
//获取插槽的数据
function getBytes32BySlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(slot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//计算储存数据插槽
function calculateLocation(uint256 slot, uint256 index) public pure returns (uint256) {
return uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot))) + index ;
}
//Hash插槽
function keccak256Slot(uint256 slot) public pure returns (uint256) {
// bytes32 paddedSlot = bytes32(slot);
bytes32 baseSlot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot));
uint256 iBaseSlot = uint256(baseSlot);
return iBaseSlot;
}
}
# Mapping
- 在定义 Mapping 类型状态变量的时候,它占用一个插槽,但不会存储任何数据
- 计算 Mapping 数据存储插槽公式:keccak256(key . slot)
- 获取数据,getBytes32BySlot(算出来的真实插槽)
- 后面看value的类型
- 计算嵌套 Mapping 数据存储插槽公式:keccak256(key2 . keccak256(key1 . slot))
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract SlotMappingExample {
uint256 a = 100; //slot 0
mapping(address => uint256) balanceOf; //slot 1;
uint256 b = 101; //slot 2;
struct User {
string name;
uint256 age;
}
mapping(address => User) public userInfo; //slot 3
mapping(uint256 => mapping(uint256 => uint256)) public score; //slot4
//设置账户
function setBalanceOf(address _address, uint256 _amount) public {
balanceOf[_address] = _amount;
}
function setUserInfo(address _address, User calldata _user) public {
userInfo[_address] = _user;
}
//设置学生信息
function setScore(uint256 _classes, uint256 _id, uint256 _score) public {
score[_classes][_id] = _score;
}
//获取插槽数据
function getBytes32BySlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(slot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//计算储存数据插槽
function calculateLocation(uint256 key, uint256 slot) public pure returns (uint256) {
return uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(key,slot)));
}
//计算储存数据插槽
//keccak256(k2 . keccak256(k1 . slot))
function calculateLocationMoreKeys(uint256 key1,uint256 key2, uint256 slot) public pure returns (uint256) {
uint256 k1Slot = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(key1,slot)));
return uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(key2,k1Slot)));
}
//Hash插槽
function keccak256Slot(uint256 slot) public pure returns (uint256) {
bytes32 baseSlot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(slot));
uint256 iBaseSlot = uint256(baseSlot);
return iBaseSlot;
}
}
# 获取插槽代码
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract SlotStringExample {
//0x48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f003c
//0x48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f303e
//0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043
string private hello = "HelloHelloHelloHelloHelloHello012"; //0x00 slot
//获取小于或等于32个字节插槽的数据
function getBytes32BySlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(slot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//获取大于32个字节的第一个插槽数据
//0x48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f48656c6c6f3031
function getFirstSlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
uint256 firstDataSlot = calculateBaseSlot(slot);
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(firstDataSlot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//获取大于32个字节的第二个插槽数据
//0x3200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
function getSecondSlot(uint256 slot) public view returns (bytes32) {
uint256 firstDataSlot = calculateBaseSlot(slot);
++firstDataSlot;
bytes32 valueBytes32;
assembly {
valueBytes32 := sload(firstDataSlot)
}
return valueBytes32;
}
//计算插槽
function calculateBaseSlot(uint256 slot) internal pure returns (uint256) {
//0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000;
bytes32 paddedSlot = bytes32(slot);
bytes32 baseSlot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(paddedSlot));
uint256 iBaseSlot = uint256(baseSlot);
return iBaseSlot;
}
}
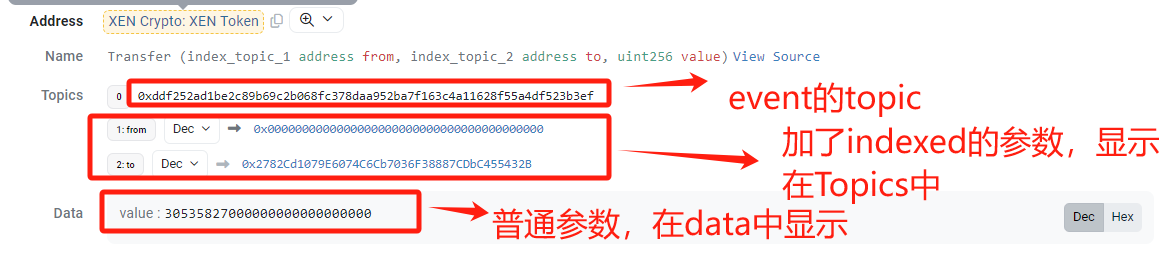
# Event
# 定义
原则上,只要往链上写数据,就要将相应数据以Logs形式写到链上去
Topics, 代表某个事件,它经过事件的名称和参数类型哈希后得到的结果
indexed, 类似关系型数据库里的索引,它能让我们快速检索到指定的数据,一个事件可以包含多次参数,但indexed最大只要3个
event Transfer();
event Transfer1(address indexed from);
event Transfer2(address indexed from,address indexed to);
event Transfer3(address indexed from,address indexed tp,uint256 amount);
event Transfer4(address indexed from,address indexed to,address indexed spender,uint256 amount);
# 提交事件
function emitTransfer() public {
emit Transfer();
}
function emitTransfer1() public {
emit Transfer1(msg.sender);
}
function emitTransfer2() public {
emit Transfer2(msg.sender,to);
}
function emitTransfer3() public {
emit Transfer3(msg.sender, to, amount);
}
function emitTransfer4() public {
emit Transfer4(msg.sender, to, spender, amount);
}
# 获取Topic的值
Topics, 代表某个事件,它经过事件的名称和参数类型哈希后得到的结果
function transferTopic() public pure returns (bytes32){
return keccak256("Transfer()");
}
function transferTopic1() public pure returns (bytes32){
return keccak256("Transfer1(address)");
}
function transferTopic2() public pure returns (bytes32){
return keccak256("Transfer2(address,address)");
}
function transferTopic3() public pure returns (bytes32){
return keccak256("Transfer3(address,address,uint256)");
}
function transferTopic4() public pure returns (bytes32){
return keccak256("Transfer4(address,address,address,uint256)");
}
# Remix控制台打印的事件
[
{
"from": "0xD7ACd2a9FD159E69Bb102A1ca21C9a3e3A5F771B",//合约地址
"topic": "0x799953580e570c6de941cdff98d09a5ad7bd20d8e32b80829cb25beb33752b09",
"event": "Transfer4",
"args": {
"0": "0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"1": "0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"2": "0xAb8483F64d9C6d1EcF9b849Ae677dD3315835cb2",
"3": "100",
"from": "0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"to": "0x5B38Da6a701c568545dCfcB03FcB875f56beddC4",
"spender": "0xAb8483F64d9C6d1EcF9b849Ae677dD3315835cb2",
"amount": "100"
}
}
]
# EthersScan查看到的日志